Identify AKI When It Matters Most
The NGAL Test allows you to know earlier so you can confidently manage your patients better.
Make Every Hour Count
By integrating damage biomarkers into clinical assessment, clinicians can discriminate AKI etiology and assess severity earlieri allowing for earlier initiation of therapies to improve patient outcomes.ii
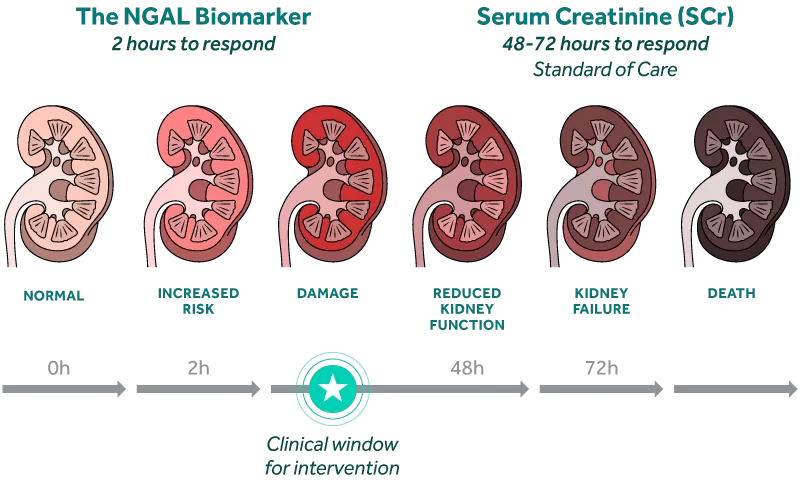
Identify AKI Days Earlier
The NGAL Test* quantifies levels of neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin (NGAL) in human urine, EDTA and heparin plasma. NGAL measurements are useful in the diagnosis of acute kidney injury which may lead to renal failure. Confidently take action to manage fluid levels, avoid nephrotoxic agents, and potentially prevent permanent kidney damage.iii
*CE-Marked in the EU; registered in Canada, Israel, Korea, and other countries.
Get Started Today
From initial exploratory meetings and clinical education to economic justifications and lab validation, the BioPorto team has experience onboarding this important assay.
With SCr, AKI Diagnosis Can Take Days
Identifying Acute Kidney Injury (AKI) early is difficult because the current standard of care relies on changes in serum creatinine and urine output, physiologic endpoints that are delayed, non-specific, and impacted by extrarenal factors such as nutrition status and muscle mass.iii

“I have changed my management decisions on rounds and definitely changed the way I approached different patients based on NGAL results.”
– PCICU Intensivist
About the Assay
A particle-enhanced turbidimetric immunoassay or the in vitro quantitative determination of neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin (NGAL). Runs on standard automated clinical chemistry analyzers.
SAMPLE TYPE
Urine or plasma
ASSAY RUN TIME
~ Approximately 10 minutes; varies by analyzer
RESULT AVAILABILITY
Similar to a comprehensive metabolic panel; varies according to your laboratory’s collection and processing schedule
The NGAL Test™ is a particle-enhanced turbidimetric immunoassay for the quantitative determination of neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin (NGAL) in human urine, EDTA plasma and heparin plasma on automated clinical chemistry analyzers. NGAL measurements are useful in the diagnosis of acute kidney injury (AKI) which may lead to acute renal failure.
* The NGAL Test is CE-Marked for in vitro diagnostic use in the European Union; registered in Canada, Korea, Israel, and several other countries.
iOstermann M, Zarbock A, Goldstein S, et al. Recommendations on Acute Kidney Injury Biomarkers From the Acute Disease Quality Initiative Consensus Conference: A Consensus Statement JAMA Netw Open. 2020;3(10):e2019209.
iiDevarajan P. Neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin: a promising biomarker for human acute kidney injury. Biomark Med. 2010;4(2):265–280.
iiiMoledina DG, Parikh CR. Phenotyping of Acute Kidney Injury: Beyond Serum Creatinine. Semin Nephrol. 2018;38(1):3–11.
ivPickering JW, Endre ZH. The definition and detection of acute kidney injury. J Renal Inj Prev. 2013 Nov 30;3(1):21-5.
