Mouse monoclonal antibody
Anti-Complement component C5b-9 (human)
CAT NO: DIA 011-01 | Application: ELISA, WB, IHC, IF
Cat. No. |
DIA 011-01 |
|---|---|
Specificity |
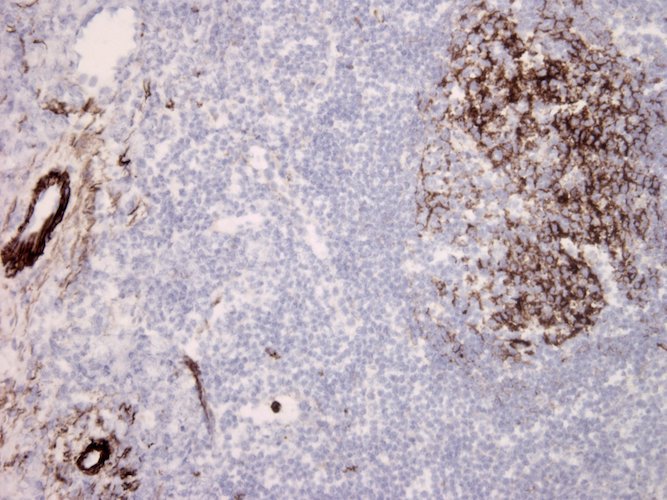
DIA 011-01 binds both membrane-bound MAC (active) and fluid-phase SC5b-9 complexes (inactive). (1) |
Immunogen |
Purified C5b-9 |
Host |
Mouse |
Positive Species Reactivity |
Human, Pig, Horse, Baboon |
Negative Species Reactivity |
Not determined |
Isotype |
IgG2a/k |
Gene ID |
727 |
Clone Number |
aE11 |
Epitope Specificity |
DIA 011-01 binds to a neoepitope exposed on C9 |
Unit Size |
400 µL: Cat. No. DIA 011-01-04 1 mL: Cat. No. DIA 011-01-1 1 mg/mL +/- 15%. See Certificate of Analysis for details. |
Purification |
Protein A/G purified (from culture supernatant) |
Form |
Liquid |
Solvent |
0.01 M phosphate buffer, pH 7.4, containing 0.15 M NaCl, 15mM NaN3 |
Conjugation |
Unconjugated BSA free |
Storage |
4-8ºC without exposure to light. No precautions necessary during handling. |
Target |
C5b-9 is also known as the terminal complement complex (TCC). The TCC consists of C5b, C6, C7, C8 and C9 and forms the membrane attack complex (MAC) as well as the non-lytic fluid-phase SC5b-9 complex (with protein S). The MAC forms channels in target cell membranes leading to cell lysis by osmotic leakage. The complexes contain neoantigens that are absent from the individual native components from which they are formed and DIA 011-01 is directed against a neoepitope exposed on C9 when incorporated into the TCC. |
Other Info |
This product is not for further manaufacture. |

